Notices for operation with O-ring
- O-ring sealing Mechanism
-
O-ring seals by using 2 main forces.
-
① Repulsive force-based o-ring compression SEAL
If O-ring is pressed and transformed, it generates a repulsive force.
Sealing is performed as O-RING groove intervals disappear.
-
② Fluid pressure-based o-ring transformation SEAL
Used fluid (liquid or gas such as oil, water, air, etc.) generates pressure to transform O-Ring.
Sealing is performed as O-Ring groove intervals disappear.
-
Compression ratio refers to O-RING compression ratio at grooves. Lower compression ratio does not give sufficient repulsive force to cause poor sealing. On the contrary, higher compression ratio is likely to damage O-RING.(see the formula below)
-
Filling ratio refers to the calculated value of O-Ring cross-section area to groove cross-section area. (see the formula below)
Lower filling ratio could cause a problem as O-ring can move inside grooves. On the contrary, higher filling ratio could damage O-RING by pushing it out from grooves or provides insufficient compression to cause poor sealing.
- How to use o-ring for movement and fixing (lateral compression)
-
For movement, operation,rotation
For fixing,(lateral compression)
Examples of cross-section standard of cylindrical face fixing/movement grooves (reference standard)
Set the groove internal diameter at an almost same value (stretches by 0.2~0.3mm) as o-ring internal diameter(ID number).
Thickness 4.0, 6.0, and 10.0 are for V series (for vacuum). No setting value for cylindrical face fixing/movement groove designing.
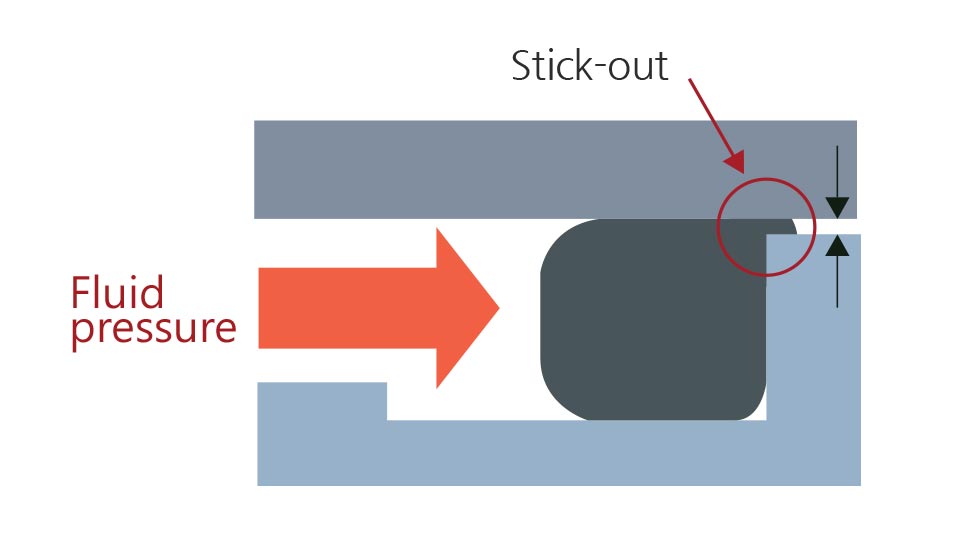
- Stick-out measure (decide whether to use Back up ring)
-
Cylindrical face fixing/movement grooves have gaps in its design structure. Depending upon groove design (max diameter groove, housing interval), used fluid pressure, o-ring hardness, etc., stick-out could take place.
Stick-out is assessed based on the following graph
In the case of stick out, the following measures could be considered; Choose an appropriate one according to situation
- · O-ring hardness change (from 70 to 90 degrees)
- · Design change (narrower groove gaps)
- · Back up ring addition (need to change groove design)
Please note that the values in the Figure does not reflect the housing expansion caused by fluid pressure.
(In general, it is recommended to consider such expansion and design gaps not exceeding 75%.)
A gap (max diameter gap) exists between outside cylindrical surface(housing) and inside cylindrical surface(rod or piston). If the gap is empty, o-ring sticks out to cause damage or leak.
-
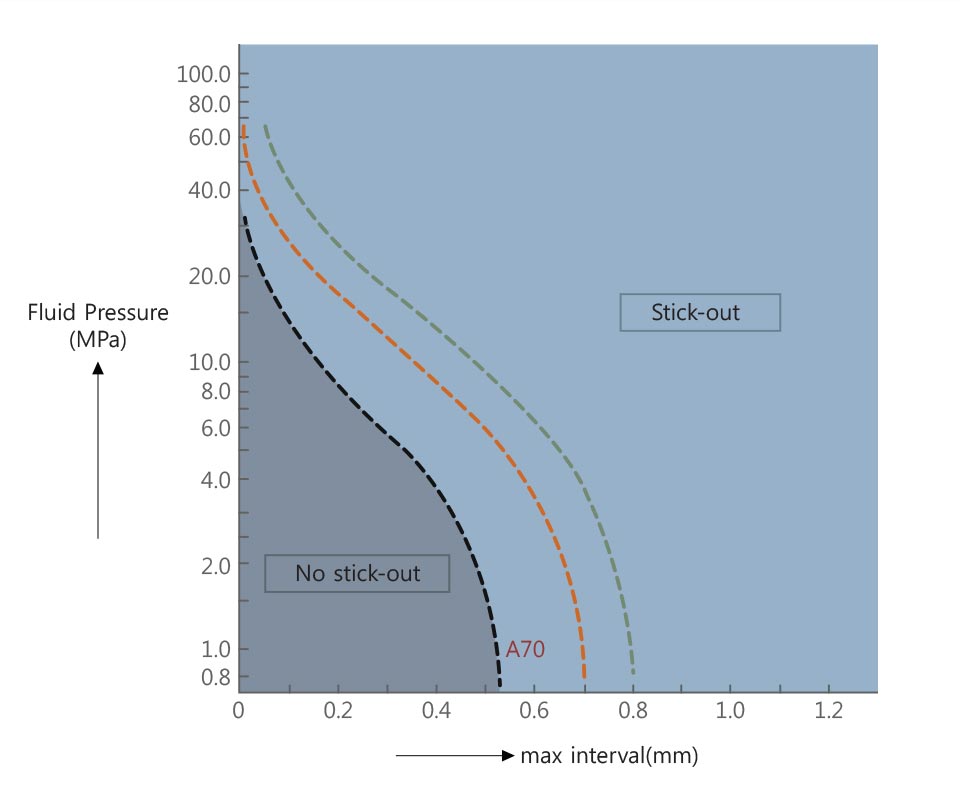
The vertical axis represents fluid pressure; horizontal axis, groove max diameter gap (housing gap). Each serves as a stick-out measurement in the cases of using hardness 70,80, and 90, and back up ring. For instance, in the Figure on the right side, if hardness is 70, the color indicates stick-out existence.
- Used for flat surface(flange) fixing
-
- Other groove design (Triangular groove, Other groove)
-
Dear visitors
Thank you for coming to the E-mos homepage. The company produces sealing-related rubber products used for semiconductors, LCD-related equipment, industrial devices, etc.
 ① Repulsive force-based o-ring compression SEAL If O-ring is pressed and transformed, it generates a repulsive force. Sealing is performed as O-RING groove intervals disappear.
① Repulsive force-based o-ring compression SEAL If O-ring is pressed and transformed, it generates a repulsive force. Sealing is performed as O-RING groove intervals disappear. ② Fluid pressure-based o-ring transformation SEAL Used fluid (liquid or gas such as oil, water, air, etc.) generates pressure to transform O-Ring. Sealing is performed as O-Ring groove intervals disappear.
② Fluid pressure-based o-ring transformation SEAL Used fluid (liquid or gas such as oil, water, air, etc.) generates pressure to transform O-Ring. Sealing is performed as O-Ring groove intervals disappear.
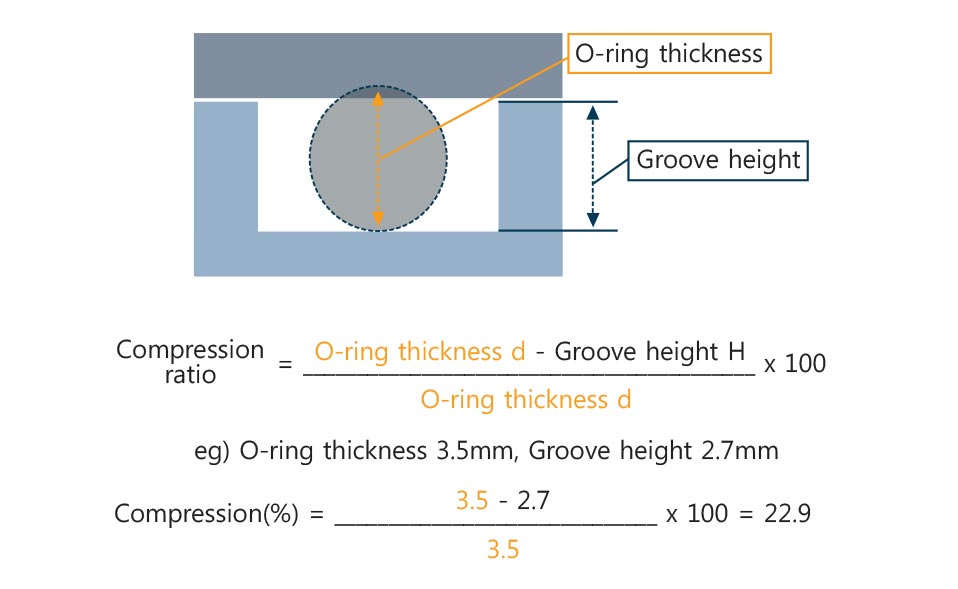 Compression ratio refers to O-RING compression ratio at grooves. Lower compression ratio does not give sufficient repulsive force to cause poor sealing. On the contrary, higher compression ratio is likely to damage O-RING.(see the formula below)
Compression ratio refers to O-RING compression ratio at grooves. Lower compression ratio does not give sufficient repulsive force to cause poor sealing. On the contrary, higher compression ratio is likely to damage O-RING.(see the formula below) Filling ratio refers to the calculated value of O-Ring cross-section area to groove cross-section area. (see the formula below) Lower filling ratio could cause a problem as O-ring can move inside grooves. On the contrary, higher filling ratio could damage O-RING by pushing it out from grooves or provides insufficient compression to cause poor sealing.
Filling ratio refers to the calculated value of O-Ring cross-section area to groove cross-section area. (see the formula below) Lower filling ratio could cause a problem as O-ring can move inside grooves. On the contrary, higher filling ratio could damage O-RING by pushing it out from grooves or provides insufficient compression to cause poor sealing.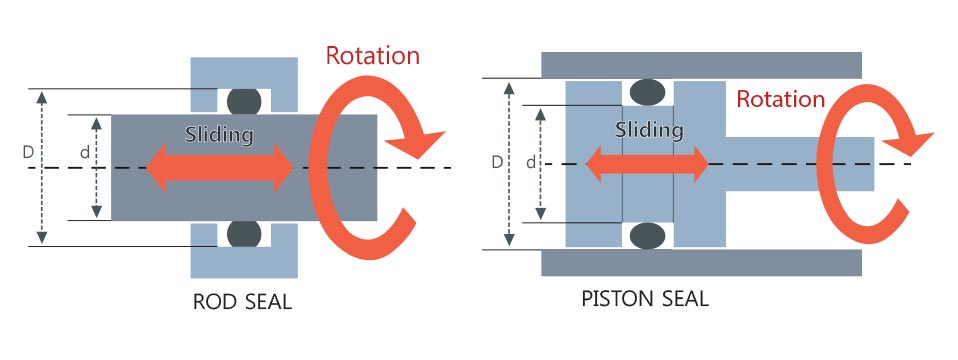
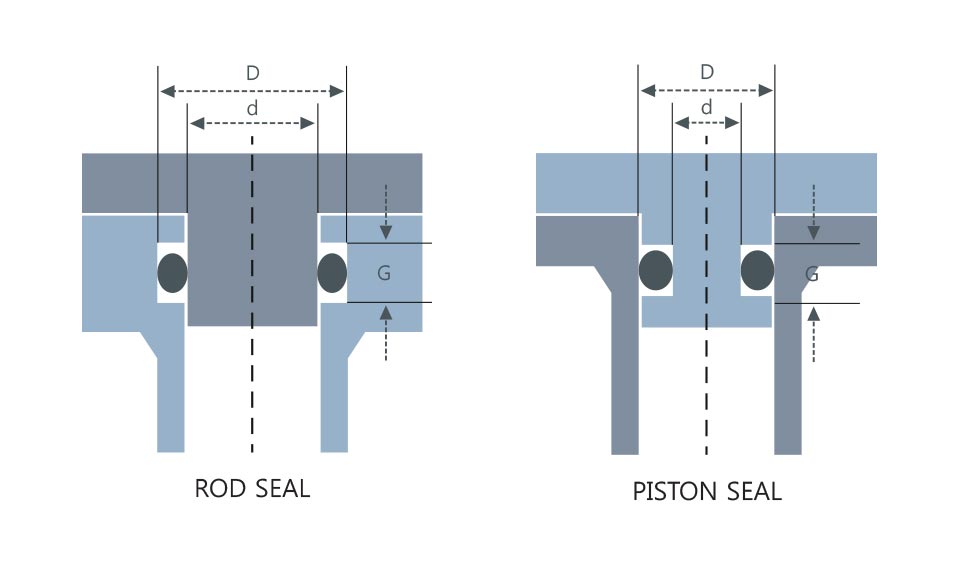

 Examples of cross-section standard of cylindrical face fixing/movement grooves (reference standard) Set the groove internal diameter at an almost same value (stretches by 0.2~0.3mm) as o-ring internal diameter(ID number). Thickness 4.0, 6.0, and 10.0 are for V series (for vacuum). No setting value for cylindrical face fixing/movement groove designing.
Examples of cross-section standard of cylindrical face fixing/movement grooves (reference standard) Set the groove internal diameter at an almost same value (stretches by 0.2~0.3mm) as o-ring internal diameter(ID number). Thickness 4.0, 6.0, and 10.0 are for V series (for vacuum). No setting value for cylindrical face fixing/movement groove designing.
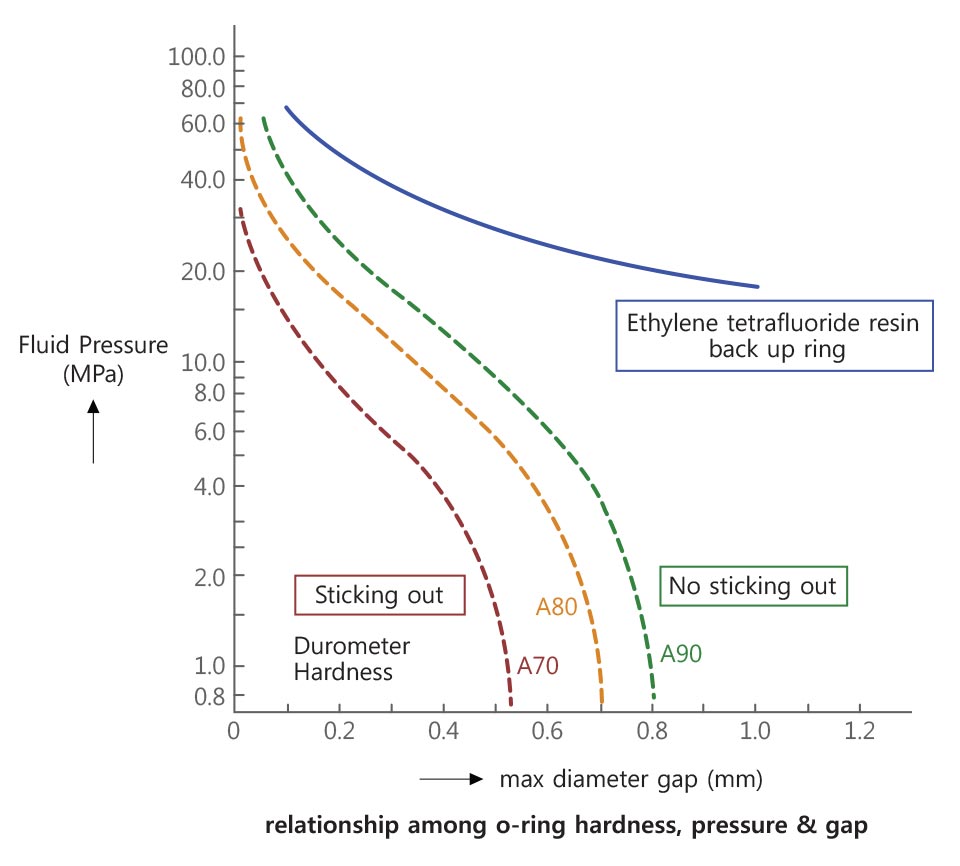
 The vertical axis represents fluid pressure; horizontal axis, groove max diameter gap (housing gap). Each serves as a stick-out measurement in the cases of using hardness 70,80, and 90, and back up ring. For instance, in the Figure on the right side, if hardness is 70, the color indicates stick-out existence.
The vertical axis represents fluid pressure; horizontal axis, groove max diameter gap (housing gap). Each serves as a stick-out measurement in the cases of using hardness 70,80, and 90, and back up ring. For instance, in the Figure on the right side, if hardness is 70, the color indicates stick-out existence.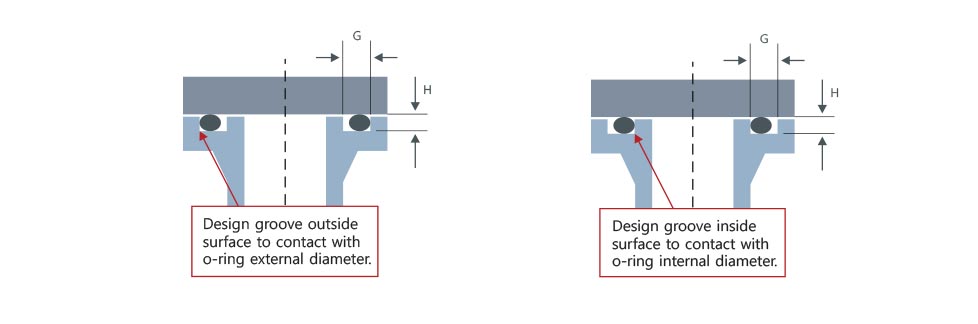
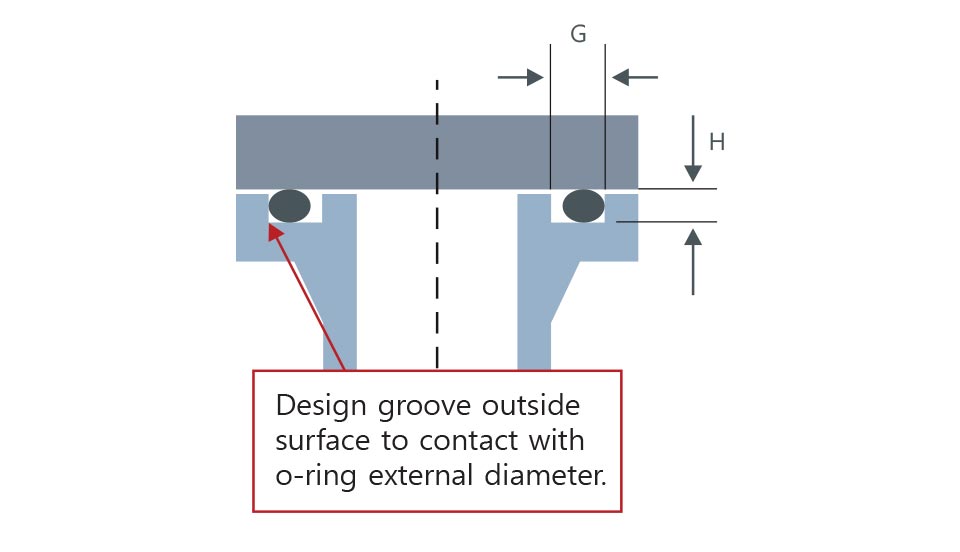 for internal pressure(high pressure)
for internal pressure(high pressure)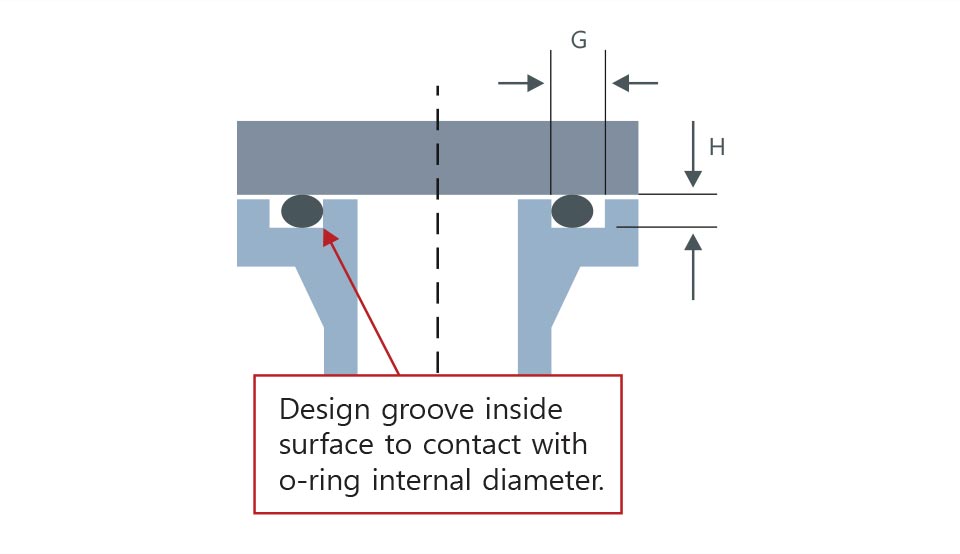 For external pressure (vacuum,decompression)
For external pressure (vacuum,decompression)
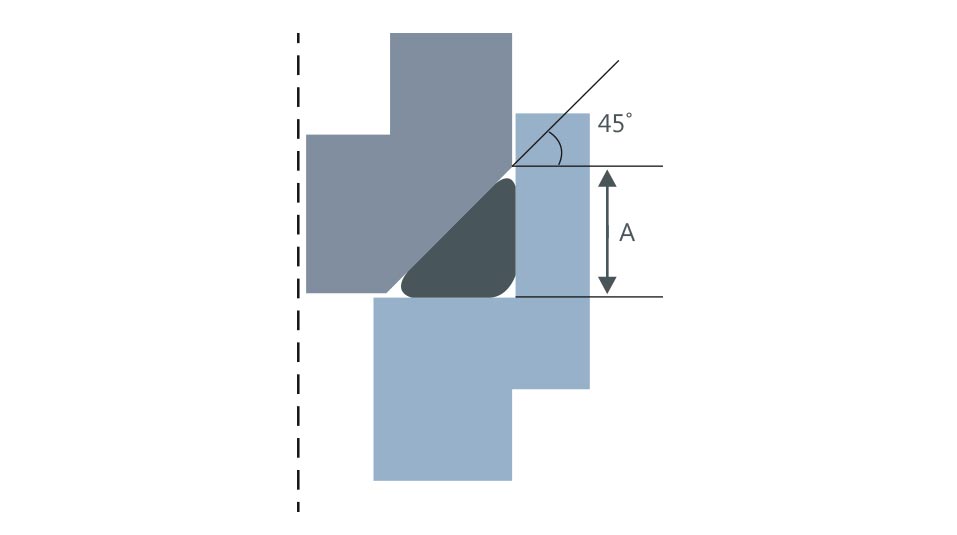 Triangular groove · Standard A is 1.3~1.4 times of o-ring thickness · 45° angle
Triangular groove · Standard A is 1.3~1.4 times of o-ring thickness · 45° angle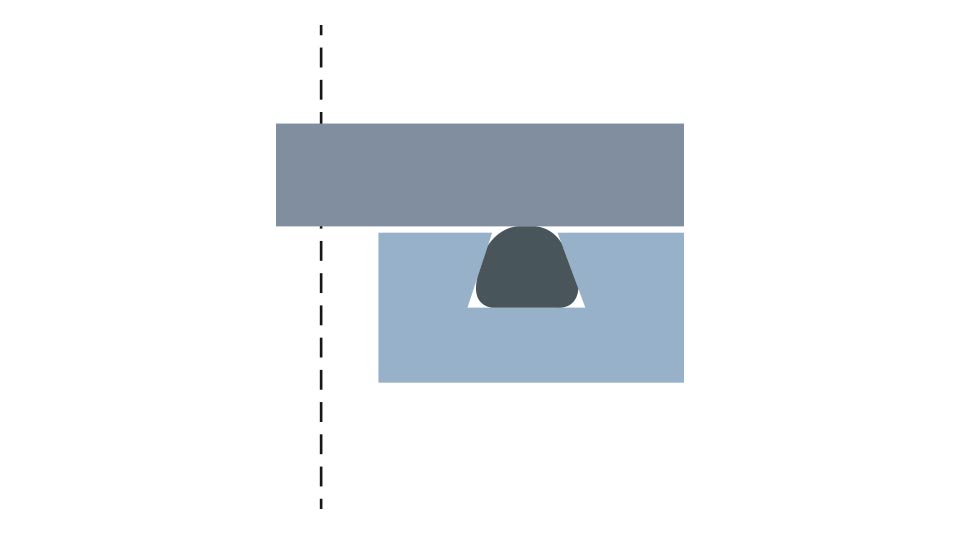 Other groove · No groove standard · Standard and shape change depending upon how to use.
Other groove · No groove standard · Standard and shape change depending upon how to use.